Manufacturing 4.0 or X.0: Digitization of industrial sector
In this article, you will learn:
-
what is Industry 4.0 and the new phrase called Industry X?
-
what has our journey to Industry 4.0 looked like?
-
are companies keen to embrace manufacturing technologies and new business models?
-
about the main areas of the fourth industrial revolution and examples of smart manufacturing solutions from Industry X offered by AIUT.
Manufacturing Industry 4.0
Manufacturing 4.0 refers to the transformation and modernization of industrial sectors through the application of digital technologies and their horizontal and vertical integration. The adopted concept aims to increase production efficiency, flexibility and to optimize manufacturing processes in factories, promoting sustainable development. Digital industrial technologies mentioned here include the integration, among others, of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, data analytics, automation, and robotics. However, it's essential to note that Industry 4.0 is not just about implemented and embedded technologies for smart factories but also involves significant systems changes in work processes and the role of humans in the industry. Hence, this industrial transformation, increasingly facilitated by advanced digital technologies that enable us to rediscover our processes in organizations, is also referred to as Industry X.

How did we find ourselves in the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Technological progress has already transformed industrial norms three times. The first major change was the invention of the steam engine in the 18th century. Its implementation in production processes ushered in the era of industrialization. This moment, or rather this industrial transformation, was named Industry 1.0.
In the 19th century, humanity discovered electricity, replacing the previously used steam engines. This led to the construction of assembly lines in factories, enabling mass production. The transformation brought about by the electrification of industry was termed the Second Industrial Revolution, or simply Industry 2.0.
The term Industry 3.0 emerged in the 1970s. More efficient computers began to appear, leading to the development of IT systems and industrial manufacturing software designed to facilitate the planning and control of manufacturing processes in production.
As one might easily guess, we have now reached Industry 4.0, whose beginnings trace back to the invention of the internet, and its development continues thanks to technological progress. Industry 4.0 integrates people and digitally controlled machines with the internet technology used in industry. All of this is done to collect, exchange, and process data from production processes, as well as to verify and reconcile the understanding of actions in factories with reality.
The ongoing and progressive digital transformation, that is, the advanced manufacturing with smart technologies that we are experiencing, is increasingly referred to as Industry X.

Are industrial manufacturing companies eager to adopt smart factory solutions? How the future of manufacturing in Poland look like?
Digitization of manufacturing and Industry 4.0 overview in Poland
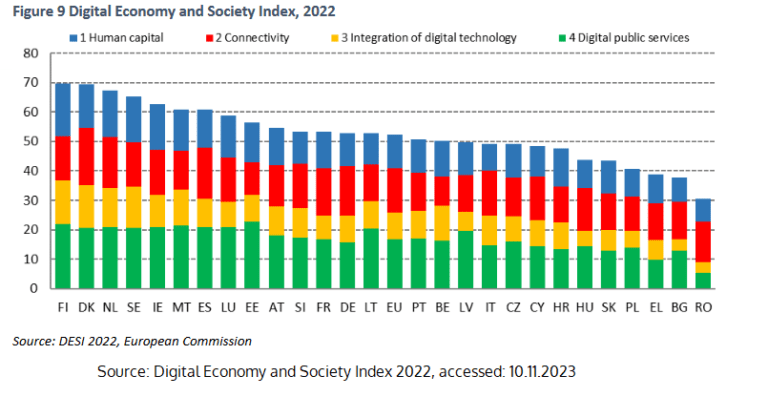
The Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI), used by the European Commission to monitor the digitalization progress of member states, reflects the advancements in Poland. According to the 2022 DESI report, Poland is developing dynamically, catching up with other European countries.
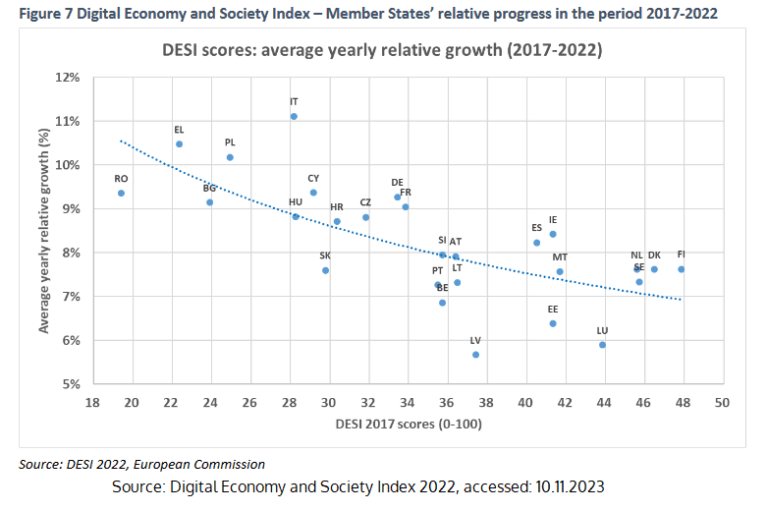
Although the DESI 2022 score for Poland was 40.5, as seen in the chart above, with the EU member states' average being 52, there is a noticeable, unexpected progress observed in the years 2017-2022 (see the chart below).
The blue line on the chart represents the estimated convergence pattern. Countries positioned above it experienced a significantly higher growth rate than expected during the years 2017-2022, thus achieving better results. Apart from Poland, these countries include Italy, Germany, Ireland, and France.
The situation of medium-sized manufacturing companies
Poland is becoming increasingly digital, and many manufacturing firms are embracing smart digital technologies, realizing the numerous benefits they bring to ensure stable and sustainable development. In the Digi Index 2023 report, Siemens pointed out the benefits associated with industrial digital transformation, such as:
- Cost savings,
- Increased production efficiency,
- Optimizing manufacturing processes,
- Enhanced safety,
- Flexible production processes,
- And reduced time to market for products.
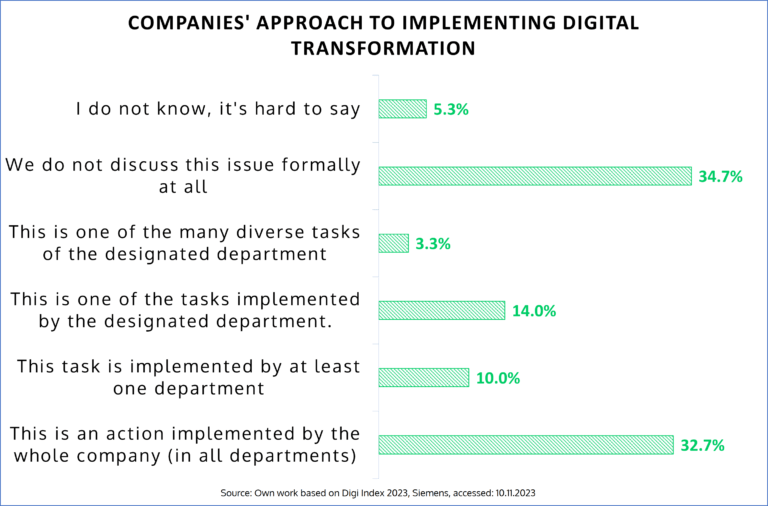
While organizations recognize these benefits, the report indicates that only 32.7% of respondents declare that digital transformation is implemented across all departments of the company. Additionally, only 12% of respondents admit that the company has widely known digital transformation strategies, while 46% do not plan to prepare such documents at all. This raises the question: what is hindering the digitization of medium-sized companies?
The most commonly indicated barriers are the lack of financial support for innovative manufacturing technologies and a lack of knowledge about the possibilities of utilizing accumulated data. Respondents also emphasize other obstacles, such as a lack of knowledge regarding the development of digital transformation strategies suitable for medium-sized companies or difficulties in integrating industrial manufacturing software from different providers.
Application of Industry 4.0 — smart manufacturing solutions
Industrial IoT (IIoT) — communication technology
One of the key elements of production digitization is the application of the Internet of Things (IoT). This allows businesses to monitor and control their production processes by collecting real-time data from sensors, for example, about performance, energy consumption, or machine status. Thanks to them, we can quickly respond to potential problems, optimize production, and minimize losses.
For example, one application of industrial IoT technology provided by the company AIUT is a remote readout system for water and heat meters based on a network of smart sensors. Other examples of using IoT technology in warehouses can be found at this link.
Industrial automation and robotics
Automation and robotics are another pillar of production digitization. The implementation of advanced systems enables the automation of manufacturing operations, leading to increased efficiency and cost reduction. Industrial robots, vision systems, and machines controlled by artificial intelligence are just a few examples of technologies revolutionizing traditional production lines.
Big Data and Machine Learning: Data collection and advanced analytics
Analytics also plays a significant role in the digitization of production. Processing vast amounts of industrial data generated by various systems allows for obtaining valuable information regarding production efficiency, trend forecasting, or identifying areas requiring optimization. This approach enables making more informed decisions and running better business processes management.
An example here could be the Real-Time Location System (RLTS). It is an indoor location system that allows real-time monitoring of industrial assets such as vehicles, individuals, or objects. It is used in factories and warehouses to verify and optimize production and intralogistics processes. Learn more.
Changes in production processes and data security
Data security is a crucial issue, especially in the era of digitization. The introduction of modern digital technologies is associated with an increased risk of cyberattacks. Therefore, manufacturing companies must invest in appropriate security measures to protect their data and maintain production continuity.

IBM MAXIMO — an example of Industry 4.0 technology
IBM Maximo is one of the world's best Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) and Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) platforms by AIUT for comprehensive enterprise resource management.
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) refers to a holistic approach to managing enterprise assets. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of assets, including planning, design, purchase, operation, maintenance, and disposal. EAM systems assist companies in tracking and optimizing the use of their assets, leading to increased operational efficiency, cost reduction, and better control over resources.
On the other hand, Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) primarily focuses on managing maintenance and reliability processes. It is a computerized system that aids in planning, monitoring, and controlling all activities related to asset maintenance. CMMS helps in scheduling maintenance work, tracking repair histories, managing spare parts inventory, and optimizing asset maintenance costs.
The integration of EAM and CMMS IT enables better management of the entire asset lifecycle, from purchase to disposal, improving maintenance and reliability planning, leading to increased asset availability and reduced downtime. It also allows effective inventory management, minimizing warehouse costs and faster response to maintenance needs.
The Maximo asset and service management system provides complete control over plant assets, enables effective work management, supports, and streamlines maintenance and service management, and documentation.
With the IBM Maximo platform, you can:
- Reduce breakdowns by up to 30%,
- Decrease downtime by 10-20%,
- Lower logistical costs by 5-20%,
- Increase asset utilization by up to 20%,
- Improve human resource utilization by up to 30%.
Other areas of manufacturing 4.0 supported by AIUT

At AIUT, we offer a full range of competencies, from mechanics and control systems to IT support, covering most areas defined by Manufacturing 4.0.
SUMMARY
Industry X is not just another stage in the industrial revolution, but also an opportunity to create more efficient, flexible, and sustainable production. By harnessing the potential of advanced manufacturing technologies, factories can not only enhance their competitiveness and build flexible processes but also begin to create intelligent industrial factories. However, it is essential to remember that the process of technological transformation is gradual and requires the workforce engagement of the entire organization.