How the EU Data Act impacts industry in the Digital Decade?
In this article, you will learn:
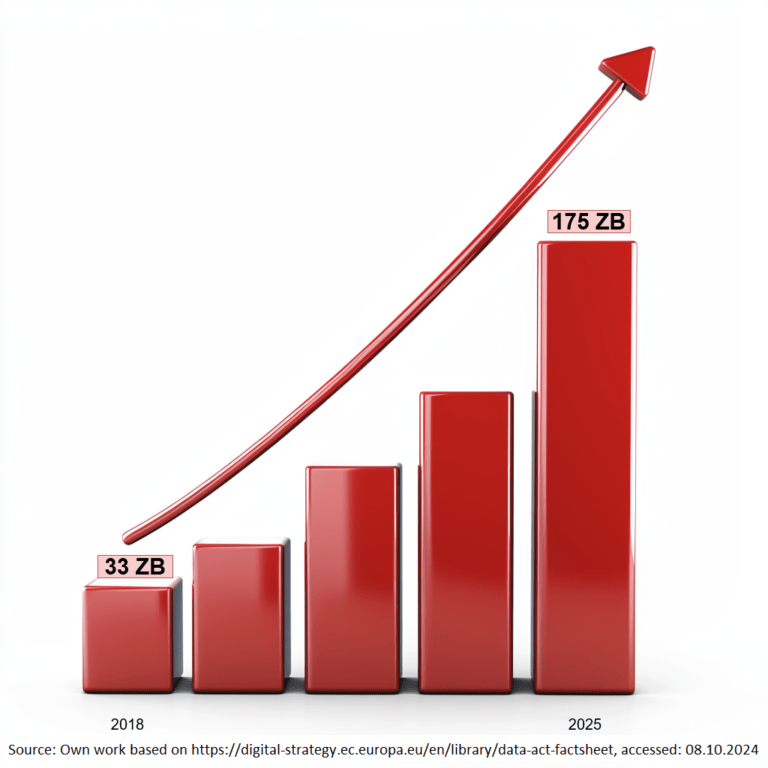
In recent years, Europe has witnessed a dynamic increase in the number of devices connected to the internet, with IoT solutions generating ever-growing datasets worldwide. Forecasts predict that the global market value of the Internet of Things (IoT) and related services will reach €11 trillion by 2030. The amount of data collected by humanity in 2018 was 33 zettabytes, and estimates suggest that this figure will rise to 175 zettabytes by 2025. This over fivefold increase creates immense potential for developing an innovative, competitive, data-driven economy. In response to the challenges of the digital world, the European Union has decided to create and implement the Data Act. In this article, we will explore what the Data Act is, what it regulates, the benefits of its implementation, and why it plays a crucial role in shaping Europe's digital future.
What is the Data Act? — key information
The Data Act is a regulation proposed by the European Commission (EC) on February 23, 2022. It complements the Data Governance Act, which, as part of the European data strategy, aims to facilitate achieving the goals outlined in the Digital Decade. The objective of the European Data Act is to define who can derive value from available data and under what conditions, as well as to establish rules for utilizing the increasing volume of data generated by Internet of Things (IoT) devices. The overarching goal is to ensure fairness in the digital world, support the development of innovative solutions, and enhance competition among entities.
The Data Act regulation came into force on January 11, 2024, and its application will begin on September 12, 2025. EU member states are required to designate appropriate authorities — either new or existing ones — responsible for implementing and enforcing the regulation. In Poland, the Ministry of Digital Affairs has already begun work on incorporating the act into Polish law. More information on this can be found here.
Benefits of implementing the Data Act
- better use of the constantly increasing amount of data
- creation of a unified data market within the EU
- ensuring fair access to data
- stimulating competition in the market
- increasing data accessibility
What does the Data Act regulate?
The Data Act regulates data exchange in three key relationships: business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), and business-to-government (B2G). These regulations aim to allow users to access and utilize data generated by Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It also mandates data sharing between businesses in situations defined by EU law and allows public sector authorities to access information held by the private sector in exceptional cases. Additionally, the regulation addresses unfair contractual terms between businesses concerning data access and usage. The Data Act also introduces measures to simplify switching between cloud service providers and promotes standards for interoperability and data processing services.

Data Act: greater control and new market opportunities. For whom?
Owners of internet-connected devices
Access to data from IoT devices gives owners the ability to monitor activities more effectively. For example, under the Data Act, at the request of a car owner with internet-connected products in their vehicle, the manufacturer will provide the generated data to a repair service chosen by the owner. This approach ensures greater control for consumers and other users of interconnected products, while also stimulating secondary market services and driving innovation.
Public sector – support in crisis management
Public sector authorities will be able to access data held by the private sector and use it to respond to public threats, such as floods or wildfires, or when the required data is not readily available by other means. If the data is essential for addressing a public threat, it will be provided free of charge. In other cases, such as preventing crises or fulfilling a public interest mandate imposed by law, the data holder may request compensation. This approach is expected to significantly improve data-driven decision-making, particularly enabling rapid and effective responses to crises such as natural disasters.
Protecting SMEs from unfair contracts
The Data Act will protect European businesses from unfair terms in data-sharing agreements imposed by one party. This will enable small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to participate more actively in the data market.
Cloud services – boosting competition and simplifying provider switching
The Data Act will allow customers to switch cloud service providers easily and free of charge. Businesses in Europe will be able to use cloud services from multiple providers simultaneously, enabling them to fully leverage the potential of the EU's cloud computing market. Costs associated with migrating data and applications between providers will be reduced, benefiting both companies and public administrations. This will also help prevent dependency on a single provider and increase competition in the market.
Protection against third-country requests – safeguarding non-personal data in the EU
The Data Act will also introduce protection against unlawful requests from third-country authorities for access to non-personal data stored in the EU, ensuring a safer and more reliable data processing environment.

The impact of the Data Act on factories: new opportunities for industry
The Data Act will open new opportunities for industry by enabling better access to data generated by industrial devices. This will allow factories to optimize their operations, production lines, and supply chain management more effectively, particularly by leveraging machine learning technologies and advanced analytics tools. The Data Act will also facilitate more flexible use of data from diverse sources and sectors, fostering greater innovation and competitiveness in the market while enabling even more precise analyses.
AIUT supports companies in fully unlocking the potential of their data by offering advanced IoT technologies. With our solutions, businesses can effectively monitor data in real-time, enabling better decision-making and process optimization. As a result, companies not only enhance their efficiency but also reduce waste, lower energy consumption, and cut CO2 emissions — key factors in achieving sustainable industrial development.

Summary
The Data Act is a key European Union regulation that redefines the rules of data access and exchange in the digital world. The regulation introduces new opportunities for businesses and the public sector, fostering innovation, competitiveness, and efficient resource management. With the Data Act, Europe emphasizes transparency, fairness, and the development of a data-driven economy.
Leverage data to optimize processes in your factory
The Data Act opens up new opportunities in data management, and AIUT is here to help you fully harness their potential. Contact us to learn how AIUT's advanced solutions can optimize your production processes, enhance efficiency, and drive innovation through data.