Industrial robots in production automation
In this article, you will learn:
-
what does the global industrial robotics market look like and how Poland is shaping its presence in it?
-
what is the industrial robot definition and how industrial robot work?
-
what are the types of industrial robots?
-
about the applications of industrial robots.
-
about the advantages of industrial robots in manufacturing facilities.
-
about the process of implementing industrial robots in collaboration with an integrator.
-
about the key aspects that ensure the productivity of robots after their deployment in a manufacturing plant.
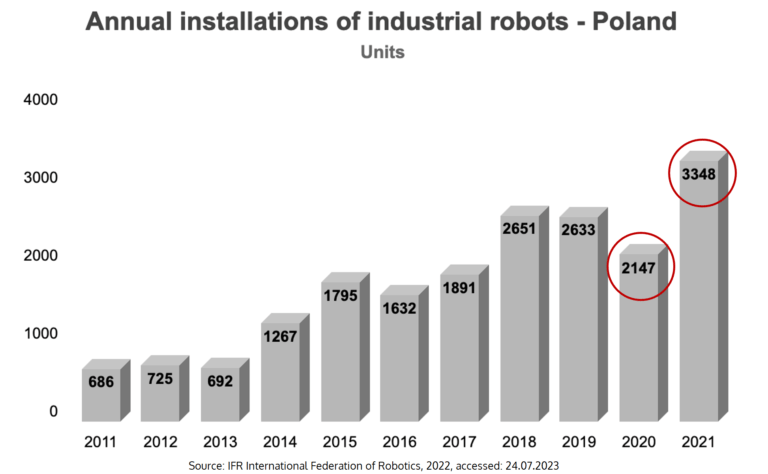
Industrial robots in factories are playing an increasingly significant role in today's production world. Equipped with modern features and technologies, these robotic machines automate and streamline various processes, enhancing productivity, precision, and flexibility. Gaining popularity, they have become an integral part of manufacturing plants worldwide. These trends are well illustrated by the latest report "World Robotics 2022" published by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR). According to the report, in 2021, 517,385 new industrial robots were installed in factories worldwide, bringing the total number to over 3.5 million units. This represented a 31% increase compared to 2020, indicating growing interest in automation and the more widespread use of robots in industrial production. The study also reveals that Poland is among the largest markets for annual installations of industrial robots, as shown in the chart below.
In Poland, the period from 2021 to 2022 is noteworthy, during which the number of new installations of industrial robots in factories increased by 56%, setting a record of 3,300 units in 2021 (see the chart below). This represents significant growth following an evident earlier slowdown in the Polish economy. So there is a question — what are industrial robots exactly, and how can they be implemented in a manufacturing facility?
Industrial robot definition
Industrial robots are programmable machines designed to perform various tasks in a manufacturing environment. They replace work that was previously done manually by humans. Industrial robots are designed in accordance with ISO 10218 – 1 and 2 standards, which apply not only to robots but also to robotic workstations and production lines, and they are harmonized with the requirements of the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC. Common types of industrial robots have a structure similar to a human arm. Equipped with advanced sensors, algorithms, and control panels, these robotic machines can operate independently, adapt to changing conditions, and perform tasks repeatedly with high precision, which can be challenging for humans to achieve.

Classification of industrial robots for manufacturing. How industrial robots work?
Industrial applications of robots are practically used in every industry and sector of manufacturing, from automobile and electronics production to pharmaceuticals and the food industry. The multipurpose industrial robots make them indispensable in many fields, leading to various classifications. For example, they can be categorized based on their functionalities, such as welding, palletizing and material handling, machine tending, or automatic assembly. On the other hand, when looking at their structure and geometric properties, there are types of robots such as Cartesian robots, articulated robots, cylindrical robots, spherical robots, SCARA robots, collaborative industrial robots (cobots), or mobile industrial robots. Additionally, they can also be grouped based on the type of drive they use – electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic – as well as their affiliation with a specific generation of robots. Furthermore, in addition to the mentioned classifications, the characteristics of manufacturing robots are adapted to various tasks in specific working conditions, such as high or low temperatures, changing humidity, contact with liquids, or clean room environments.

Industrial robot applications – examples
Industrial modern robots create standalone (stationary or mobile) production stations, or their potential can be used to build entire production lines. A robotic workstation means that at least one manufacturing robot is located in a single production cell, performing a specific assigned task. When thinking about robotic production lines, the entire project is treated as one giant machine consisting of many processes and robots.
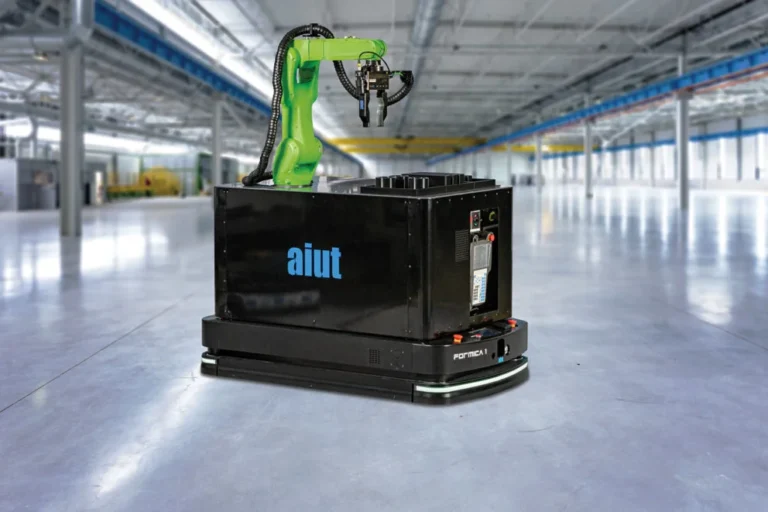
An example of a mobile production station by AFORMIC is the autonomous mobile platform FORMICA 1. It is integrated with a collaborative industrial robot (cobot), which allows the platform to perform production tasks autonomously on its own deck. The robot arm, which is integrated with a platform (see the picture below), enables the placement of products directly retrieved from the shelf onto the vehicle's deck and unloading at a designated location, with adjustments in behavior when working alongside a human operator. Such applications of collaborative industrial robots enable the automation of processes in the area of internal logistics. Learn more about the benefits of using our mobile production station (mobile industrial robots) here.

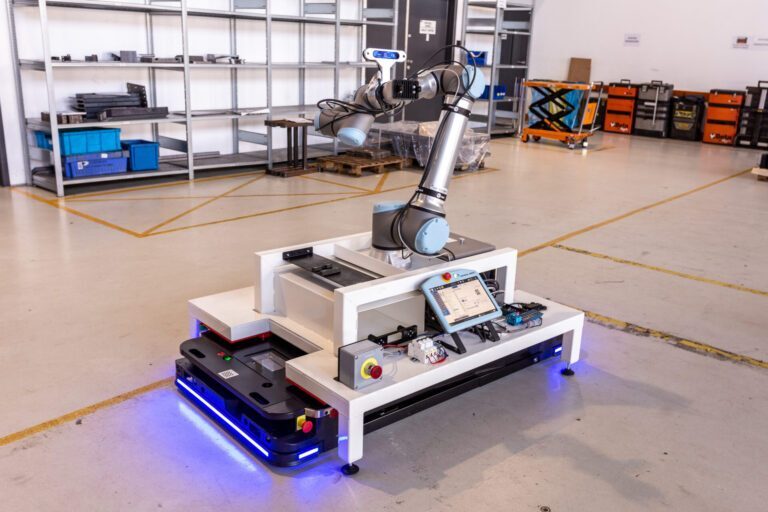
Another example of production robots is the latest solution for autonomous inspection using a cobot and an AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot) by AFORMIC. CoRiser is a robotic, mobile platform that oversees other autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and production lines, supporting maintenance work in manufacturing facilities. Watch a short video about the CoRiser solution to learn more.

Benefits of using industrial robots
Robots increase productivity and operational efficiency
First and foremost, automating production processes using robots contributes to a significant reduction in costs and an increase in operational efficiency. The productivity of robots is immense because, unlike humans, they can work 24/7. Furthermore, these multipurpose industrial robots can adapt to various types of production and meet changing market demands. Also, with them, you can meet your manufacturing goals.

A solution to workforce shortages
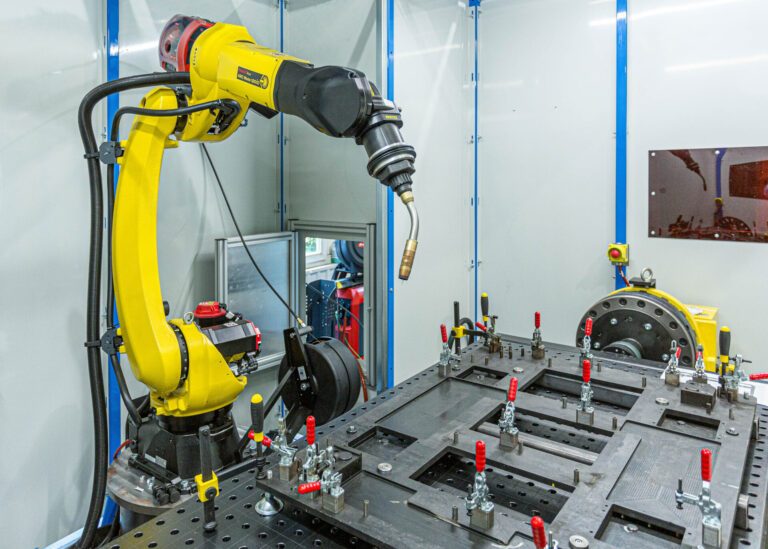
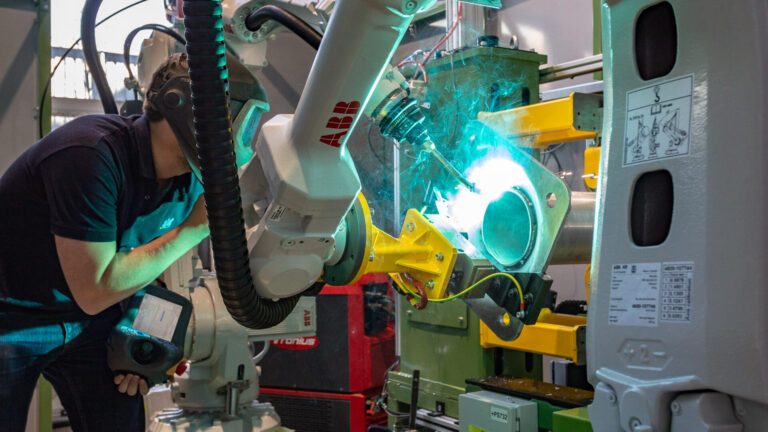
The introduction of industrial robots also helps solve manufacturing challenges such as labor shortages, as they can replace humans in various job positions. Thanks to them, factories can maintain uninterrupted operations even in the case of unforeseen events, such as increased employee absences, as witnessed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Advanced manufacturing robots, for example, welding (see the picture below) and painting robots, can also compensate for a lack of qualified specialists.

Improving workplace safety
Furthermore, manufacturing robots are utilized to work in hazardous conditions, resulting in improved workplace safety and hygiene. For example, they can perform tasks related to lifting heavy components as they have a big load capacity or operate in environments where aggressive chemicals harmful to human health are present.

Ensuring high-quality products
Production robots can replace humans in simple and repetitive tasks, and provide high-precision processes. Therefore, this allows employees to be assigned to more creative duties. By programming precisely industrial robot movements and adapting them to perform various tasks, human errors are eliminated, material losses are minimized, and production standardization is introduced. In this way, automated functionality ensures high product quality, which results in generating savings for factories.

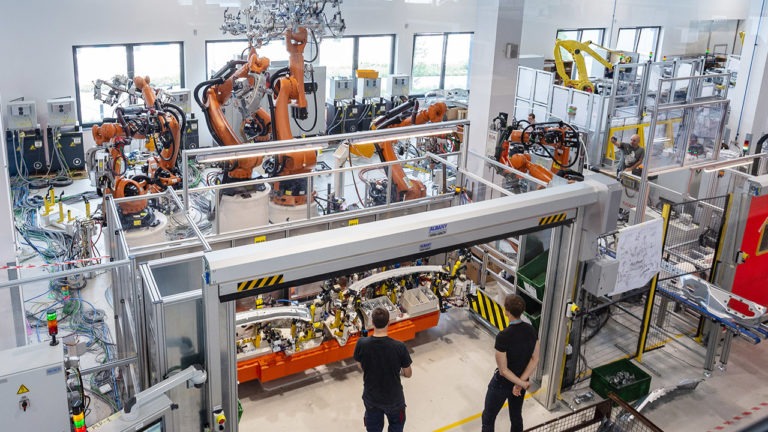
The process of introduction industrial robots in a manufacturing facility
In addition to the numerous benefits that come with the use of modern robots in production, adopting industrial robots also involves several challenges, such as proper testing of designed robots, ongoing maintenance, and servicing. Below, we have outlined what each stage of the implementation process looks like with us – the integrator of solutions in the field of industrial automation and robotics.
1. Identifying customer needs and defining the project scope
The project execution starts with identifying the customer's needs. We gather project data, establish its purpose, and define the final outcomes based on defined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) used to evaluate the quality of the implementation.
2. Technical project preparation
In the next phase, we proceed to select the manufacturing robot and prepare the technical project. This stage includes technical and economic analysis, process simulations, the development of various mechanical, electrical, and robot software projects, as well as placing orders for equipment from suppliers – industrial robot manufacturers.
3. Machine construction and commissioning at our production facilities
The next step involves building the workstations or production lines, commissioning the machine, and conducting a comprehensive assessment of the solution, along with implementing any necessary improvements. In our case, the construction and refinement of the solution take place first at our company's facilities.
4. Implementation at the customer's site
Next, we move on to the actual implementation phase at the customer's site, where we transport the machine and integrate it with existing equipment. After completing the optimization process, the workstation or production line is handed over to the customer, and the industrial robot is ready for use.

Key aspects that ensure continued productivity of robots in the factory
Pre-implementation stage
Throughout the entire process of implementing industrial robots, collaboration between the integrator and the client's services is crucial because it's the client who takes over the workstation/production line and needs to understand how the entire system functions. According to us, a key aspect is the pre-implementation stage, which involves testing the designed solutions. At AIUT, thanks to our own production facilities and appropriate systems, we can create simulations, and digital twins, and test entire production lines through virtual commissioning. Watch the video to see how it looks at our place. This action minimizes the risk of errors during actual implementation, making the startup of such tested and programmed industrial robots at the client's site simply shorter.
Integration of solutions
The second aspect to remember is the integration of industrial robots with solutions that enable machine communication with management systems. The client must provide a system that aggregates and analyzes individual data and effectively manages the production or warehouse process. Regular reports will provide the plant with information about what happened with a product on the production line or a mobile robot during its operation, allowing for process optimization.
Service and maintenance
The third very important aspect is the maintenance and post-warranty service of robots. To make the investment in modern robots pay off and to avoid production downtime, it's essential to regularly inspect and service the robots in accordance with the industrial robot manufacturer's recommendations. Depending on the type of robot, this may involve tasks such as lubricating all joints, replacing batteries, and drive belts, and checking for clearances, or drives. At AIUT, our strategy is based on building local engineering centers in our client markets. This allows us to quickly respond in the event of a breakdown in our client's facility and regularly service the equipment. Thus, it enables us to ensure optimal robot performance and minimize production downtime risks.

Summary
Automation with advanced industrial robots is a crucial element of modern manufacturing processes. The operation of industrial robots in factories ensures production continuity, which is particularly significant because the industry dislikes downtime. The use of production robots becomes indispensable for companies aiming to improve safety, ensure high quality, increase productivity and profitability, and maintain competitiveness in the market. The diversity of industrial robots ranges offers vast possibilities for industrial applications, which is a crucial step towards more efficient production.

Explore industrial robots for manufacturing and implement them with us into your industrial sector.
As an experienced integrator of automation and industrial robotics solutions, we design, manufacture, and deliver turnkey robotic workstations and production lines to a high standard. We provide support at every stage of investment preparation. If you are planning to implement an industrial robotic solution, talk to our experts today.